THIS POST INCLUDES:
- Art Therapy and Loneliness
- About the Client
- Art Therapy Exercise
- Client Insight and Outcomes
- Disclaimer
- FREE DOWNLOAD Art Therapy Exercise
ART THERAPY AND LONELINESS
Loneliness is a universal human experience that can deeply impact one’s emotional well-being. It is a state of feeling disconnected or isolated from others, and it can occur due to various circumstances such as the loss of a loved one, fractured family dynamics, a change in social environment, or a lack of meaningful relationships.
Loneliness is not merely an emotional state; it has profound implications for our overall well-being. The negative impacts on mental health, physical health, and cognitive function highlight the urgent need to address loneliness at both individual and societal levels. Creating supportive environments, promoting social inclusion, and implementing interventions that foster meaningful connections are vital steps in combating loneliness.
Psychological research has deepened our understanding of loneliness as a complex human experience. By identifying its causes, exploring its effects, and developing effective strategies to address it, we can work towards building a more connected and compassionate society. Loneliness should be seen not as an inevitable aspect of human existence but as a challenge that can be overcome through intentional efforts, support systems, and a reimagining of our social fabric.
CHARACTERISTICS OF LONELINESS
Loneliness can manifest in different ways for different individuals, but some common traits include:
- Emotional Distress: Loneliness often accompanies a range of negative emotions such as sadness, despair, and anxiety. It can create a deep sense of emptiness and longing for companionship.
- Social Isolation: Loneliness can lead to withdrawal from social interactions and a feeling of being disconnected from others. It may result in limited social connections and difficulties in forming new relationships.
- Negative Self-Perception: People experiencing loneliness may develop negative beliefs about themselves, feeling unworthy of love and companionship. This negative self-perception can further perpetuate feelings of isolation and hinder efforts to seek support.
CAUSES OF LONELINESS
Loneliness can arise from various factors, both internal and external. Psychologists have identified several common causes:
- Social Isolation: Physical separation from others due to geographic distance, lack of social networks, or limited opportunities for social interaction can contribute to loneliness.
- Relational Factors: Loneliness can stem from unsatisfying or strained relationships, lack of emotional intimacy, or feelings of social rejection.
- Life Transitions: Significant life changes, such as relocation, retirement, or the loss of a loved one, can trigger feelings of loneliness as familiar social connections are disrupted.
- Individual Differences: Certain personality traits, such as introversion or social anxiety, may predispose individuals to experience loneliness.
EFFECTS OF LONELINESS
Loneliness can have far-reaching effects on our mental, emotional, and physical well-being:
- Mental Health: Research has consistently linked loneliness to increased risk of mental health issues, including depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. Chronic loneliness can also contribute to cognitive decline and difficulties in emotion regulation.
- Physical Health: Loneliness has been associated with a range of physical health problems. Studies suggest that lonely individuals have a higher likelihood of developing cardiovascular diseases, compromised immune function, and sleep disturbances.
- Cognitive Function: Loneliness can impact cognitive processes, such as attention, memory, and decision-making. It can lead to cognitive biases, social withdrawal, and difficulties in social perception.
- Mortality: Loneliness has been linked to increased mortality risk. The negative impact on overall health suggests the need to address loneliness as a public health concern. This is especially relevant as some communities become more insulated from developing strong connections and social cohesion.
STRATEGIES TO OVERCOME LONELINESS
Psychological research offers several strategies to address and mitigate feelings of loneliness:
- Cultivating Social Connections: Actively seeking out social opportunities, engaging in activities aligned with personal interests, and building meaningful relationships are crucial steps in combating loneliness. Joining clubs or community groups and participating in social events can help expand social networks.
- Enhancing Social Skills: Developing effective communication and interpersonal skills can bolster the ability to form and maintain satisfying relationships. Training programs and therapy can provide guidance and support in improving social skills.
- Online and Virtual Communities: The advent of technology has provided new avenues for connection. Online communities, support groups, and social media platforms can help individuals combat loneliness by connecting with like-minded individuals.
- Therapy and Counseling: Professional help from therapists or counselors can be instrumental in addressing loneliness. These professionals provide a safe and supportive environment to explore and resolve underlying issues contributing to loneliness.
- Self-Care and Wellness: Prioritizing self-care is essential in combating loneliness. Engaging in activities that promote well-being, such as exercise, mindfulness, and hobbies, can improve self-esteem, reduce stress, and enhance overall satisfaction with life.
- Mindset Shift: Developing a positive mindset and challenging negative thoughts related to loneliness can be transformative. Building self-compassion, practicing gratitude, and focusing on personal growth and fulfillment can help reshape one’s perspective.
HOW ART THERAPY CAN HELP WITH LONELINESS
Art therapy provides a safe and supportive space for individuals to express themselves creatively, explore their emotions, and develop a deeper understanding of their experiences. Art therapy can offer unique benefits in addressing loneliness including:
- Emotional Expression: Art allows individuals to express their emotions in a non-verbal and symbolic manner. For those struggling with loneliness, creating art can serve as a channel to communicate their innermost feelings, which may be difficult to articulate verbally.
- Self-Exploration and Insight: Engaging in the art-making process can foster self-reflection and introspection. By exploring their loneliness through art, individuals can gain new insights into their experiences, uncover underlying issues, and develop a greater sense of self-awareness.
- Transformation: Creating art can provide a sense of relief, enabling individuals to process their loneliness and begin the healing process. The act of transforming emotions through creating art can be empowering and insightful when a client makes connections between their external experiences and how it affects their internal feelings.
- Connecting with Others: Group art therapy sessions can create a sense of community and connection. Sharing artwork and personal stories with others who have similar experiences of loneliness can foster empathy, support, and a sense of belonging.
THE ROLE OF THE ART THERAPIST
In the context of addressing loneliness, the art therapist plays a crucial role in guiding and facilitating the therapeutic process. The art therapist employs their expertise in both art and psychology to create a supportive environment for clients. Some key responsibilities of the art therapist include:
- Creating a Safe Space: The art therapist establishes a safe and non-judgmental space where clients can freely express themselves. Trust and confidentiality are essential to fostering a therapeutic alliance.
- Guidance: The art therapist guides clients in exploring various art techniques and mediums. They provide suggestions and support to help clients translate their emotions and experiences into visual representations.
- Facilitating Reflection and Insight: Through open-ended questions and reflective discussions, the art therapist encourages clients to explore the themes and symbolism present in their artwork. This process promotes self-discovery and deeper understanding.
- Supporting Emotional Processing: The art therapist offers emotional support throughout the art therapy journey. They help clients navigate difficult emotions that may arise during the creative process and provide strategies for managing distress.
ABOUT THE CLIENT
- Name: Leanne
- Age: 62
CURRENT CLIENT ISSUES:
Leanne recently retired from her long career as a teacher. Since leaving work, Leanne has been feeling a deep sense of loneliness. Leanne realised her colleagues formed her social network and without them she has not developed friendships outside of work. Leanne reached out to an art therapist in hopes of finding a way to cope with her loneliness and rediscover a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
ART THERAPY EXERCISE
The art therapy exercise designed for Leanne focused specifically on her experience of loneliness. The goal was to provide her with a means of expressing her emotions and exploring ways to cope with her feelings of isolation.
INSTRUCTIONS:
- Theme and Symbolism: Leanne was encouraged to think about the theme of loneliness and consider visual symbols that resonated with her experience. She was invited to explore images, words, and colours that evoked emotions or represented her aspirations for connection.
- Reflective Dialogue: After completing her collage, Leanne engaged in a dialogue with the art therapist. They discussed the symbols, colours, and overall composition of the artwork, allowing Leanne to share her insights and emotions that emerged during the creative process.
CLIENT INSIGHT AND OUTCOMES
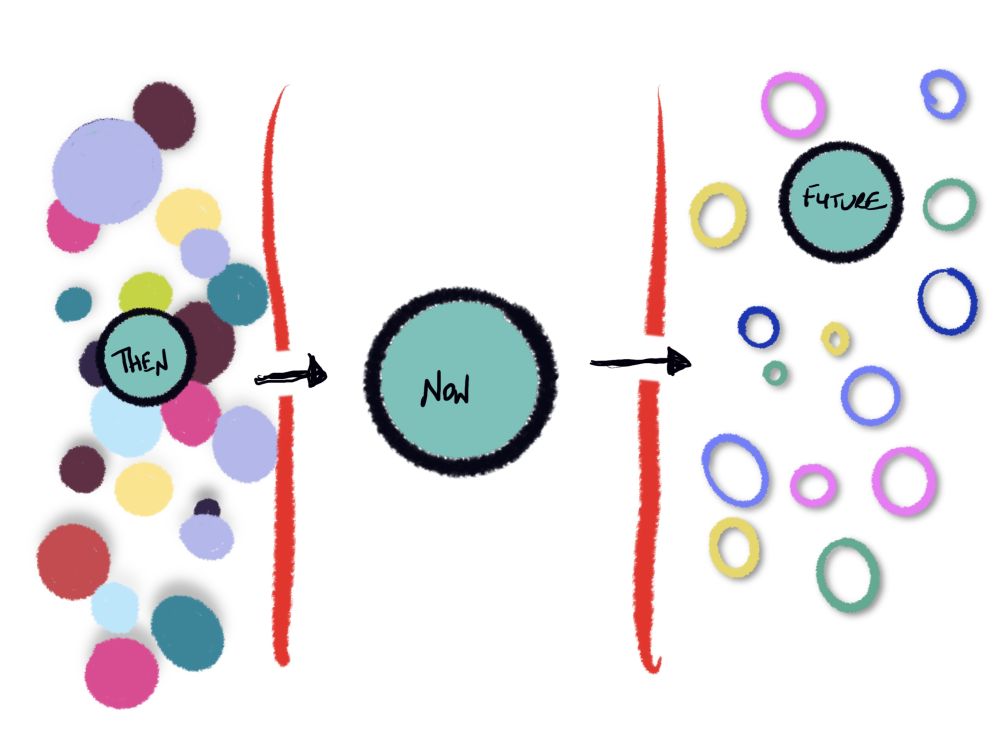
Leanne found she gained a new perspective on her loneliness and discovered how she had experienced connection before when she was working and could seek that connection again. As Leanne created her artwork, she realized that her loneliness was not solely rooted in the loss of her job but also in her own self-perception. She recognized that she had neglected her own needs and desires, focusing solely on work relationships. This insight opened up a path for self-discovery and self-care that Leanne could pursue other avenues to develop new friendships outside of a career.
Throughout the process of creating art, Leanne felt she was able to release her grief, sadness, and longing. This emotional release brought a sense of relief and lightness. Leanne gained new perspectives on her loneliness and identified that she could undertake some changes in a simplified way as her artwork represented.
DISCLAIMER
This case study represents a snapshot of the client’s progress in treatment. The exercise in this article could be used as written or as a guide for new and original tasks developed by the Art Therapist. Responsibility for treatment resides with the individual therapist who understands their clients specific needs. The art therapy exercise should not be viewed as a pre-defined directive on how to treat a client that presents with a specific range of problems.This art therapy exercise will help build a database of knowledge to draw upon when helping your client. Art Therapy is associated with psychotherapy techniques, however each therapist often approaches therapy with their own foundation of psychological interventions, whether it be psychotherapy, CBT, DBT or other methods.
FREE DOWNLOAD: Art Therapy Exercise
Download the FREE Art Therapy Exercise based on the above Case Study. The free download includes instructions for the art therapy exercise, along with an example of the art therapy exercise.

BUILD YOUR ART THERAPY REFERENCE MATERIALS:
Pin this image to your Pinterest board.

SHARE KNOWLEDGE & PASS IT ON:
If you’ve enjoyed this post, please share it on Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest. Thank you!
